Ubuntu 14.04下Django和MySQL环境部署全过程
简要步骤。(Ubuntu14.04)
- Python安装
- Django
- Mysql的安装与配置
记录一下我的部署过程,也方便一些有需要的童鞋,大神勿喷~
一、Python环境搭建
操作系统Ubuntu14.04,自带Python2.7.6
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
im@58user:/$ python
Python 2.7.6 (default, Oct 26 2016, 20:30:19)
[GCC 4.8.4] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
|
二、Django环境搭建
目前Django的版本已经到1.11了。先去官网下载Linux对应的文件,然后解压&安装。(官网下载地址)
|
1
2
3
|
tar xzvf Django-1.11.x.tar.gz
cd Django-1.11.x
sudo python setup.py install
|
这时可能会提示ImportError: No module named setuptools
执行
|
1
|
sudo https://bootstrap.pypa.io/ez_setup.py -O - | sudo python
|
然后执行
|
1
|
python setyp.py install```
|
到此Django安装成功~!
三、Mysql安装
执行一下命令,运行过程中可能需要输入root密码并进行确认。
|
1
2
|
sudo apt-get install mysql-server mysql-client
sudo apt-get install libmysqld-dev
|
然后链接MySQL和Python
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
sudo apt-get install python-dev
sudo wget https://pypi.python.org/packages/source/M/MySQL-python/MySQL-python-1.2.5.zip
unzip MySQL-python-1.2.5.zip
cd MySQL-python-1.2.5/
sudo python setup.py install
|
进入mysql数据库的方式:
|
1
2
3
|
> * sudo mysql
* mysql -u root -p
然后输入密码
|
四、给mysql设置root密码
先以第一种方式进入mysql
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
mysql> use mysql;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> update user set Password = PASSWORD(‘root') where User ='root';
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 3 Changed: 3 Warnings: 0
mysql> exit
|
括号里面的'root'就是新的密码
五、新建项目
到了验证结果的时候了
将当前目录切换到Python的worspace下,输入新建的项目名称:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
im@58user:~/PythonProjects$django-admin.py startproject Hello
im@58user:~/PythonProjects$ cd Hello/
im@58user:~/PythonProjects/Hello$ tree
├── Hello
│ ├── init.py
│ ├── settings.py
│ ├── urls.py
│ └── wsgi.py
└── manage.py
|
- * __init__.py:Python特性,可以是空文件,表明这个文件夹是一个可以导入的包。
- * settings.py:配置文件,本文主要修改数据库信息、模板目录、加载模块的信息。
- * url.py:URL配置文件,指定函数与URL的映射关系。
- * wsgi.py:本文中不会使用,nginx/apache+wsgi在生产环境中运行Django时使用
接下来我们写一个HelloWorld页面。
在Hello文件下的一级目录创建views.py文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
im@58user:~/PythonProjects/Hello$ touch views.py
im@58user:~/PythonProjects/Hello$ ls
Hello manage.py views.py
im@58user:~/PythonProjects/Hello$ tree
.
├── Hello
│ ├── init.py
│ ├── settings.py
│ ├── urls.py
│ └── wsgi.py
├── manage.py
└── views.py
1 directory, 6 files
|
在views.py文件中写入下面代码
|
1
2
3
4
|
from django.http import HttpResponse
def hello(request):
return HttpResponse(“Hello World~!~!”)
|
然后再将路径添加在urls.py文件中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from views import hello
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^admin/‘, admin.site.urls),
url(r'^hello/‘, hello),
]
|
然后在Hello目录下执行python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8080
启动服务器
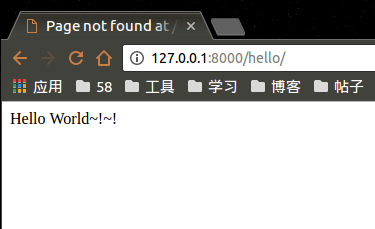
打开浏览器访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/hello/ 可以看到展示结果。
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作能带来一定的帮助,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流。
本文由主机测评网发布,不代表主机测评网立场,转载联系作者并注明出处:https://zhujiwo.jb51.net/ubuntu/4056.html

